Connecting two or more computers/hardware devices through
communication channels so that they can communicate and share files, documents, commands, data, etc., including the hardware and software
resources.
Uses of Computer Network:
- It allows you
to share resources such as printers, scanners, etc.
- You can share
expensive software and database among network users.
- It facilitates
communications from one computer to another computer.
- It allows the
exchange of data and information among users through a network.
Types of Computer Networks in use today:
- Local Area
Network (LAN)
- Metropolitan
Area Network (MAN)
- Wide Area
Network (WAN)
- Personal Area
Network (PAN)
- Wireless Local
Area Network (WLAN)
- Campus Area
Network(CAN)
- Storage-Area
Network(SAN)
- System Area
Network
- Passive
Optical Area Network
- Enterprise
Private Area Network
- Virtual
Private Network
Now let's discuss all these in details
Local Area Network (LAN):
The local area network is a computer network that operates
in a small area, i.e., it connects computers in a small geographical area like
within an office, company, school, or any other organization.
A local area network may be a wired or wireless network or a combination of both. The devices in a LAN are generally connected using an Ethernet cable, which offers an interface to connect multiple devices like routers, switches, and computers.
For example, using a single router, few Ethernet cables, and computers, you can
create a LAN at your home, office, etc. In this network, one computer may act
as a server and other computers, which are part of the network, may serve as
clients.
Topologies of LAN:
Topology:
It refers to the arrangement of computers (nodes) in a computer network. The
main topologies of a local area network are as follows:
Ring Topology:
The computers are connected in a circular and closed-loop in
a ring topology. The message in this topology moves only in one direction
around the ring from one node to another node and is checked by each node for a
matching destination address. So, the data keeps moving until it reaches its
destination. All nodes are equal; a client-server relationship does not exist
between them. As the nodes are in the form of a ring, if one node fails to
transmit the data, the flow of communication is severed.
Star Topology:
In this, all the computers are separately connected to a central node or
connection point, which can be a server, a hub, a router, or a switch. This
topology offers an advantage that if a cable does not work, only the respective
node will suffer, the rest of the nodes will work smoothly. All data or
messages that one node sends to another passes through the central hub.
This
topology is easy to design and implement as well as it is easy to add
additional nodes to the central node. The major drawback of this topology is
that it is prone to bottleneck or failure at the central connection point,
i.e., failure at the central node will affect the entire communication.
Bus Topology:
In this topology, the computers are connected through interface connectors
to a single communication line (central cable) that carries the message in both
directions. The central cable to which all the nodes are connected is the
backbone of the network. It is called a bus. The signal in this arrangement
travels in both directions to all the machines until it finds the recipient
machine. It is easy to set up than other topologies as it uses only a single
central cable to establish the network.
Advantages of LAN:
- It offers a
higher operating speed than WAN and MAN.
- It is less expensive and easy to install and maintain.
- It perfectly
fulfils the requirement of a specific organization, such as an office,
school, etc.
- It can be
wired or wireless or a combination of both.
- It is more
secure than other networks as it is a small set-up that can be easily
taken care of.
Primary Functions of LAN:
- Sharing of
files: It allows you to share or transfer files
from one computer to another computer within the LAN. For example, in a
bank, it can be used to send a file with the details of transactions of a
customer from the server to clients.
- Sharing of printers: It also allows shared access to a
printer, file servers, etc. For example, ten computers that are connected through LAN can use a single printer, file server, fax machine, etc.
- Sharing of
Computational capabilities: It allows the clients to access the computational power of a server, e.g.,
an application server as some applications which run on clients in a LAN
may require higher computational capabilities.
- Mail and
message related services: It allows sending and receiving mails between computers of a LAN. You are required to have a mail server for this.
- Database
services: It also allows storing and retrieving data with the help of a database server.
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN):
MAN is a high-speed network that spreads over a large geographical area such as a metro city or town. It is set up by connecting the local area networks using routers and local telephone exchange lines.
It can be operated by a private
company or it may be a service provided by a company such as a local telephone
company.
MAN is ideal for the people of a relatively large area who want to share data or information. It provides fast communication via high-speed carriers or transmission media such as copper, fibre optics, and microwaves.
The commonly
used protocols for MAN are X.25, Frame Relay, Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM),
xDSL (Digital Subscriber Line), ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network),
ADSL (Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line), and more.
The
area covered by MAN is larger than the LAN but smaller than a WAN. Its network
ranges from 5 to 50 km. Furthermore, it also provides uplinks for connecting
LANs to WANs and the internet. An organization can use a MAN to connect all of
its LANs located at its different offices across the city.
Examples of MAN:
- Cable TV
Network
- Telephone
service provides that provide high-speed DSL lines
- IEEE 802.16 or
WiMAX
- Connected fire
stations in a city
- Connected
branches of a school in a city
Advantages of MAN:
- Less
Expensive: It is less expensive to set up a MAN and
to connect it to a WAN.
- High Speed: The speed of data transfer is more than WAN.
- Local Emails: It can send local emails fast.
- Access to the
Internet: It allows you to share your internet
connection, and thus multiple users can have access to high-speed
internet.
- Easy to set
up: You can easily set up a MAN by connecting multiple LANs.
- High Security: It is more secure than WAN.
Wide Area Network (WAN):
WAN
extends over a large geographical area. It is not confined within an office,
school, city, or town and is mainly set up by telephone lines, fibre optic, or
satellite links. It is mostly used by big organizations like banks and
multinational companies to communicate with their branches and customers across
the world. Although it is structurally similar to MAN, it is different from MAN
in terms of its range, e.g., MAN covers up to 50 Kms, whereas WAM covers
distances larger than 50 Km, e.g., 1000km or more.
A WAN
works by using TCP/IP protocol in combination with networking devices such as
switches, routers, firewalls, and modems. It does not connect individual computers;
rather, they are designed to link small networks like LANs and MANs to create a
large network. The internet is considered the largest WAN in the world as it
connects various LANs and MANs through ISPs.
The
computers are connected to the wide-area network through public networks, such
as telephone systems, leased lines or satellites. The users of a WAN do not own
the network as it is a large setup connecting the remote computer systems.
However, they are required to subscribe to a service provided by a telecommunication
provider to use this network.
Advantages of a WAN:
- Large Network
Range: It spans a large geographical area of
2000 km or more, e.g., from one country to another countries.
- Centralized data: It allows your different office branches to use your head office server for retrieving and sharing data. Thus, you don't need to buy email servers, files servers and backup servers, etc.
- Get updated
files and data: It provides an ideal platform for companies who need a live server for their employees to exchange updated files within seconds.
- High
bandwidth: It offers high bandwidth than a normal broadband connection. Thus, it can increase the productivity of your company by offering uninterrupted data transfer and communication.
- Workload
Distribution: It helps distribute your workload to other locations. You can hire employees in different countries and assign them to work from your office.
Examples of WAN:
Internet
US defense department
Stock exchanges network
Railway reservation system
Big Banks' cash dispensers' network
Satellite systems
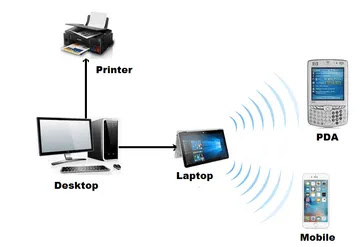
Personal Area Network (PAN)
The smallest and most basic type of network, a PAN is made up of a
wireless modem, a computer or two, phones, printers, tablets, etc., and revolves
around one person in one building. These types of networks are typically found
in small offices or residences and are managed by one person or organization
from a single device.
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN)
Functioning like a LAN, WLANs make use of wireless network
technology, such as Wi-Fi. Typically seen in the same types of applications as
LANs, these types of networks don’t require that devices rely on physical
cables to connect to the network.
Campus Area Network (CAN)
Larger than LANs, but smaller than metropolitan area networks (MANs,
explained below), these types of networks are typically seen in universities,
large K-12 school districts or small businesses. They can be spread across
several buildings that are fairly close to each other so users can share
resources.
Storage-Area Network (SAN)
As a dedicated high-speed network that connects shared pools of storage
devices to several servers, these types of networks don’t rely on a LAN or WAN.
Instead, they move storage resources away from the network and place them into
their own high-performance network. SANs can be accessed in the same fashion as
a drive attached to a server. Types of storage-area networks include converged,
virtual and unified SANs.
System-Area Network (also known as SAN)
This term is fairly new within the past two decades. It is used to
explain a relatively local network that is designed to provide high-speed
connection in server-to-server applications (cluster environments), storage
area networks (called “SANs” as well) and processor-to-processor applications.
The computers connected on a SAN operate as a single system at very high
speeds.
Passive Optical Local Area Network (POLAN)
As an alternative to traditional switch-based Ethernet LANs, POLAN
technology can be integrated into structured cabling to overcome concerns
about supporting traditional Ethernet protocols and network applications such
as PoE (Power over Ethernet). A point-to-multipoint LAN architecture, POLAN
uses optical splitters to split an optical signal from one strand of single
mode optical fibre into multiple signals to serve users and devices.
Enterprise Private Network (EPN)
These types of networks are built and owned by businesses that want to
securely connect its various locations to share computer resources.
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
By extending a private network across the Internet, a VPN lets its users
send and receive data as if their devices were connected to the private network
– even if they’re not. Through a virtual point-to-point connection, users can
access a private network remotely.




















1 Comments
Nice
ReplyDelete